Skewness is a measure of how much a cell deviates from an ideal shape. It is one of the most important indicators of mesh quality, as highly skewed cells can reduce the accuracy and stability of the numerical solution. Skewness is defined differently for different types of cells, such as triangles, tetrahedra, hexahedra, or polyhedra. In general, skewness is calculated as the difference between the shape of the cell and the shape of an equilateral cell of equivalent volume. The skewness value ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 means no skewness and 1 means maximum skewness. A good mesh should have low skewness values for most of the cells.
In ANSYS Mechanical and CFD, you can check the skewness of your mesh using various methods. For example, you can use the Report Quality button in the General task page to print a message to the console that shows the maximum cell skewness in your mesh. You can also use the Equivolume Skewness option in the Mesh Metric dropdown list in the Mesh Control task page to display a contour plot of the skewness on your mesh3. You can also use the Mesh Quality Criteria dialog box to set the minimum acceptable skewness value for your mesh and generate a report that shows how many cells violate this criterion.
There are different ways to improve your mesh quality and reduce the skewness in ANSYS. Here are some suggestions that you can try:
- Modify your geometry to avoid sharp angles, small gaps, or thin features that can cause highly skewed cells. You can use the Geometry tool in ANSYS to edit your model and simplify it if possible.
- Choose an appropriate element type for your mesh, such as tetrahedra, hexahedra, or polyhedra. Different element types have different skewness definitions and criteria. Generally, hexahedral elements have lower skewness than tetrahedral elements, but they are more difficult to generate for complex geometries. Polyhedral elements can adapt to any geometry and have lower skewness than tetrahedral elements, but they require more memory and computational time.
- Adjust your element size to balance between accuracy and efficiency. A smaller element size can capture more details of the geometry and the physics, but it can also increase the number of cells and the skewness. A larger element size can reduce the number of cells and the skewness, but it can also lose some important information and introduce errors. You can use the Size Function option in ANSYS Meshing to control the element size based on various criteria, such as curvature, proximity, or sphere of influence.
- Apply different meshing methods to different parts of your geometry, such as patch conforming, patch independent, or cutcell. Different meshing methods have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of quality, speed, and robustness. You can use the Method option in ANSYS Meshing to select the best meshing method for each part of your model.
- Refine your mesh based on the change in cell volume or the gradient of cell volume. This can improve the smoothness of your mesh and reduce the skewness. You can use the Refinement option in ANSYS Meshing to refine your mesh based on various criteria, such as face size, face proximity, or face curvature.
You can check the skewness of your mesh using various methods in ANSYS Mechanical and CFD. For example:
- You can use the Report Quality button in the General task page to print a message to the console that shows the maximum cell skewness in your mesh.
- You can use the Equivolume Skewness option in the Mesh Metric dropdown list in the Mesh Control task page to display a contour plot of the skewness on your mesh.
- You can use the Mesh Quality Criteria dialog box to set the minimum acceptable skewness value for your mesh and generate a report that shows how many cells violate this criterion.
There are other ways to improve the skewness factor besides the ones I mentioned in my previous response. Here are some additional suggestions that you can try:
- Use the skewness correction option in ANSYS Meshing to automatically adjust the node positions of highly skewed cells. This option can improve the skewness of tetrahedral and hexahedral elements by moving the nodes along the edges or faces of the cells1.
- Use the smoothing option in ANSYS Meshing to iteratively relocate the nodes of the mesh to optimize the cell quality. This option can reduce the skewness of tetrahedral, hexahedral, and polyhedral elements by minimizing the distortion of the cells2.
- Use the inflation option in ANSYS Meshing to create a boundary layer mesh near the walls or boundaries of your geometry. This option can improve the skewness of tetrahedral and polyhedral elements by creating prism or pyramid elements near the walls, which have better alignment with the flow direction3.
I hope these suggestions help you further improve your skewness factor in ANSYS. 😊
If U want to read more interesting tips and tutorials try links below
Cooling process of the gear on Transient Thermal (Ansys Workbench)
What is Ansys Speos and how to use
What is Young Modulus in Ansys Mechanical (impact of this factor for structural analysis)
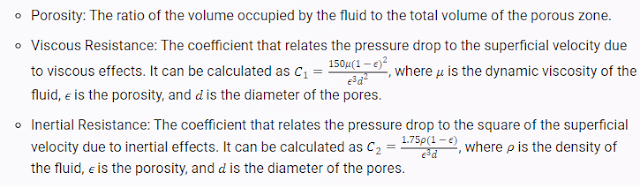
How to define porosity (porous medium) in Ansys CFD (Fluent, CFX)