Meshing is one of the decisive steps in both CFD and FEA analysis. The correct execution of the mesh and optimization in terms of the number of finite elements makes the work of every Ansys user much easier.
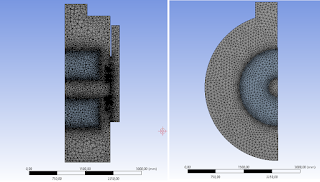 |
| Example of CFD mesh in Ansys Workbench |
The quality of the mesh will determine the speed of convergence of the partial equations and the correctness of the obtained distributions (in terms of physical phenomena). Optimization for the number of finite elements will shorten the entire calculation process while maintaining the correctness of the model. Also, an extremely important aspect (if there is such a possibility in the analyzed model) is the selection of the appropriate type of finite element. But we will deal with this in the following entries.
In this post, the general principles of discretization method in CFD simulations will be presented.
First of all U need to simplify the geometry of the model. Delete all irrelevant elements that will not affect the physics of the analyzed phenomenas. Try to delete micro and mini elements, chamfers, fillets etc.
Under meshing u need to follow two basic (general) rules:
1) try to avoid empty regions in the computational domains
2) Check that Ur model doesn't have overlapping elements (U can generate mesh quality to see this error)
After that U must following by the goal function - MESH QUALITY (computational cost). Very good otion to optimize this is to make sensivity analysis where U check imbalances which are dependent from element size, element type and time step size.
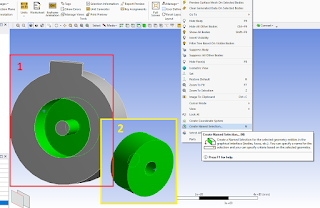 |
| Correct faces pick in Ansys Meshing |




No comments:
Post a Comment